

My local AI stack
Update August 2025
I've upgraded this guide to a simpler form, using official Llama.cpp Docker image, and adding some new tools like Qwen Code or OpenCode, and defaulting to the new Qwen3-coder-30A3B LLM which is heavier (30B) but faster (A3B) here is the post :
Introduction
I've used many dozens of hours trying a lot of tools to have an easy to use AI stack that fully runs on my machine.
Powered with llama.cpp, I have an extensible Open Web UI frontend, code completion with Tabby, code assistance with avante.nvim, I can also play with bolt.diy and Comfy UI but I mainly use the former.
Create a directory to host all this stuff, I will use `~/ai-stack` in this article
mkdir ~/ai-stack
cd ~/ai-stack
# for the models, build deps and docker volumes
mkdir models build data
# and init a git repo
git init
# ignore secrets and data dirs
echo -e ".env.*\nmodels\ndata" > .gitignoreLlama.cpp : the backend
First thing there is to get and build llama.cpp
# let's not pollute the root dir, clone into build/
git clone https://github.com/ggml-org/llama.cpp build/llama.cppI use Linux and have an Nvidia GPU (RTX 3090). If you have a mac or another type of GPU need to head to https://github.com/ggml-org/llama.cpp?tab=readme-ov-file#supported-backends and check the compilation flag you need to build llama.cpp.
For Nvidia - you obviously need the CUDA toolkit (https://developer.nvidia.com/cuda-downloads) - it is as simple as
cd build/llama.cpp
cmake -B build -DGGML_CUDA=ON
cmake --build build --config ReleaseYou now have several binaries built, that share most of the launch arguments.
Text completion
I prefer to use env variables that will be easier to use with Docker, we'll see that later.
In my example I will use Qwen 2.5 Coder 14b as main model and the 0.5b one as a draft model.
We won't be downloading Qwen's own uploaded weights as they are not in the llama.cpp's format, which is GGUF, so you can go to Bartowski's page and download the gguf file that will not saturate your GPU (there is a table detailing the sizes).
It is not recommended to go below Q4 quants if you can't fit them into your GPU, use a smaller model, the quality is usually too low but it depends on many factors
Download a model and the 0.5b one as draft, and put them in a models directory inside llama.cpp
# enable flash attention
LLAMA_ARG_FLASH_ATTN=1
# fully load model into GPU
LLAMA_ARG_N_GPU_LAYERS=999
# main model
LLAMA_ARG_MODEL=models/qwen2.5-coder-14b-instruct-q6_k.gguf
# draft model to speed up tokens/second (speculative decoding)
LLAMA_ARG_MODEL_DRAFT=models/Qwen2.5-Coder-0.5B-Instruct-Q6_K.gguf
# draft model settings (suggested value)
LLAMA_ARG_DRAFT_MAX=16
# draft model settings (suggested value)
LLAMA_ARG_DRAFT_MIN=5
# fully load draft model into GPU
LLAMA_ARG_N_GPU_LAYERS_DRAFT=999
# ROPE allow to drastically increase the context window
LLAMA_ARG_ROPE_SCALING_TYPE=yarn
# by a factor of 4 (!!)
LLAMA_ARG_ROPE_SCALE=4
# type of compression for context
LLAMA_ARG_CACHE_TYPE_K=q4_0
LLAMA_ARG_CACHE_TYPE_V=q4_0
# base context that will be multiplied by 4, that is 128k context
LLAMA_ARG_CTX_SIZE=32768
Now, let's launch the server with those params :
LLAMA_ARG_FLASH_ATTN=1 \
LLAMA_ARG_N_GPU_LAYERS=999 \
LLAMA_ARG_MODEL=models/qwen2.5-coder-14b-instruct-q6_k.gguf \
LLAMA_ARG_MODEL_DRAFT=models/Qwen2.5-Coder-0.5B-Instruct-Q6_K.gguf \
LLAMA_ARG_DRAFT_MAX=16 \
LLAMA_ARG_DRAFT_MIN=5 \
LLAMA_ARG_N_GPU_LAYERS_DRAFT=999 \
LLAMA_ARG_ROPE_SCALING_TYPE=yarn \
LLAMA_ARG_ROPE_SCALE=4 \
LLAMA_ARG_CACHE_TYPE_K=q4_0 \
LLAMA_ARG_CACHE_TYPE_V=q4_0 \
LLAMA_ARG_CTX_SIZE=32768 \
./llama-server
Loading the model takes a few dozens of seconds, when you see :
main: server is listening on http://0.0.0.0:8080 - starting the main loop
you can go to http://localhost:8080 and see the basic web UI that llama.cpp embeds.
You can try to chat, play with settings, I personally ticked "Show tokens per seconds" in "Advanced" as I like stats.
Embedding
You will need to start a 2nd instance of llama-server to embed code, it will allow Tabby to import some of your codebases (or any Github/Gitlab/website) to improve code completion, I downloaded an embedding model : https://huggingface.co/nomic-ai/nomic-embed-text-v1.5-GGUF (I picked the .f16 one, which as the best quality and has a size of 274MB. Put it next to the two other models, then launch a second llama-server instance :
LLAMA_ARG_N_GPU_LAYERS=999 \
LLAMA_ARG_MODEL=/models/nomic-embed-text-v1.5.f16.gguf \
LLAMA_ARG_CTX_SIZE=2048 \
LLAMA_ARG_EMBEDDINGS=1 \
LLAMA_ARG_NO_WEBUI=1 \
LLAMA_ARG_PORT_PORT=8081
./llama-server
Code completion : Tabby
On their Github, their is a one liner to lauch Tabby with Docker.
Before using it, we need to tell Tabby to use our llama.cpp backend :
mkdir ~/.tabby
touch ~/.tabby/config.toml
# use your favorite text editor to put this into config.toml
[logs]
level = "debug"
[model.completion.http]
kind = "llama.cpp/completion"
# this does not matter, it's managed by llama.cpp
model_name = "qwen2.5-coder:14b-instruct-q8_0"
api_endpoint = "http://llama:8080"
prompt_template = "<|fim_prefix|>{prefix}<|fim_suffix|>{suffix}<|fim_middle|>"
[model.chat.http]
kind = "openai/chat"
model_name = "qwen2.5-coder:14b-instruct-q8_0"
api_endpoint = "http://llama:8080"
[model.embedding.http]
kind = "openai/embedding"
model_name = "Nomic-Embed-Text"
api_endpoint = "http://llama:8081"
Tabby by default runs on :8080 as llama.cpp, so we will update the Docker command to use our config, update the listening port and get rid of CUDA options as we don't want Tabby to manage the model :
docker run -it \
-p 8082:8080 -v $HOME/.tabby:/data \
tabbyml/tabby \
serve Now head to http://localhost:8082 to create an account and check that Tabby is running.
You can test the connection to llama in the first box :
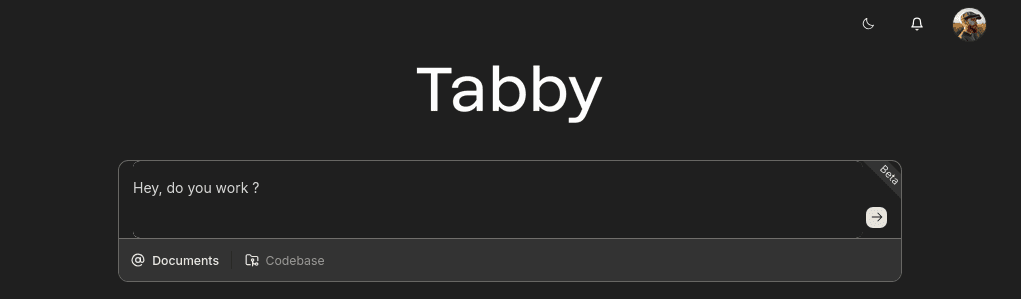
Text editor plugin
Tabby has plugins for Vim/Neovim, Eclipse, VSCode and IntelliJ, click on the link that suits your editor to get started.
Note that you want to point your config to http://localhost:8082 where tabby is listening.
For my Neovim using Lazy as a plugin manager, it is as simple as this :
{
"TabbyML/vim-tabby",
lazy = false,
dependencies = {
"neovim/nvim-lspconfig",
},
init = function()
vim.g.tabby_agent_start_command = { "npx", "tabby-agent", "--stdio" }
vim.g.tabby_inline_completion_trigger = "auto"
vim.g.tabby_inline_completion_keybinding_accept = "<C-CR>"
end,
}
You can check your tabby agent config in ~/.tabby-client/agent/config.toml, make sure the server's endpoint is on localhost on port 8082.
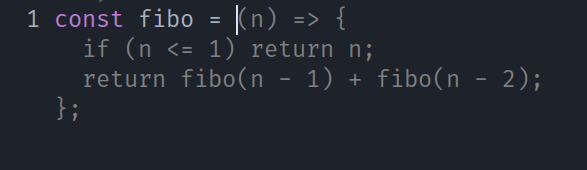
And that's it, I now have some code completion updating on text input, that I accept with Control+Enter
Open WebUI : advanced UI
Now, there are several UIs for text and chat completion that are better than the default llama-server UI, I've chosen Open WebUI for its extensibility via plugins and tools.
There is a one liner there too :
docker run -d -p 3000:8080 \
-e OPENAI_API_BASE_URL=http://localhost:8080/v1 \
-v open-webui:/app/backend/data \
--name open-webui \
--restart always \
ghcr.io/open-webui/open-webui:mainYou can check you localhost on port 3000 : http://localhost:3000 and onboard. It should detect the model running on you llama-server.
There are lots of settings but don't tinker yet, this is just a test, we are gonna drop the data volume :)
There is an official extensions store at https://openwebui.com/ and I encourage you to check them.
Docker Compose
Ok what a nice stack we have, but what happens when you reboot ? Or some new versions are released ? (OK this is not so bad with the actual stack and the `restart: always` given to Docker, but there is a simpler way (I think) : the Compose way.
First, let's create a folder to store some config and data, I will be using `~/ai` :
cd ~/ai-stack
touch docker-compose.yml
# this will come handy to manage several configs
touch .env.webui
touch .env.llama-qwen-14b
touch .env.embedding
# for open webui persistance
mkdir data/openwebui
# convert our llama.cpp into a git submodule
git submodule add https://github.com/ggml-org/llama.cpp build/llama.cpp/ Llama.cpp
I've tried the official docker image but it was out of date, so we will build it with Compose, just to test, you can run those commands
# adapt to where you cloned it
cd build/llama.cpp
git pull
# there are several dockerfiles for different architectures, pick the good one
docker build -t llama -f .devops/cuda.Dockerfile .
In the docker-compose.yml, let's setup llama (adapt the volume line, the first part is your host download folder, the right part must not change), the deploy block is for Nvidia GPU, you'll find how to adapt it to any other architecture if you need to.
services:
llama:
build:
context: ./build/llama.cpp/
dockerfile: .devops/cuda.Dockerfile
env_file: .env.llama-qwen-14b
restart: always
container_name: llama
ports:
- 8080:8080
volumes:
- ./models:/models
deploy:
resources:
reservations:
devices:
- driver: nvidia
device_ids: ['0']
capabilities: [gpu]
embedding:
build:
context: ./build/llama.cpp/
dockerfile: .devops/cuda.Dockerfile
env_file: .env.embedding
container_name: embedding
restart: always
ports:
- 8081:8080
volumes:
- ./models:/models
deploy:
resources:
reservations:
devices:
- driver: nvidia
device_ids: ['0']
capabilities: [gpu]
Add this to .env.llama-qwen-14b
LLAMA_ARG_FLASH_ATTN=1
LLAMA_ARG_N_GPU_LAYERS=999
LLAMA_ARG_MODEL=/models/qwen2.5-coder-14b-instruct-q6_k.gguf
LLAMA_ARG_MODEL_DRAFT=/models/Qwen2.5-Coder-0.5B-Instruct-Q6_K.gguf
LLAMA_ARG_DRAFT_MAX=16
LLAMA_ARG_DRAFT_MIN=5
LLAMA_ARG_N_GPU_LAYERS_DRAFT=999
LLAMA_ARG_ROPE_SCALING_TYPE=yarn
LLAMA_ARG_ROPE_SCALE=4
LLAMA_ARG_CACHE_TYPE_K=q4_0
LLAMA_ARG_CACHE_TYPE_V=q4_0
LLAMA_ARG_CTX_SIZE=32768
And this for .env.embedding
LLAMA_ARG_N_GPU_LAYERS=999
LLAMA_ARG_MODEL=/models/nomic-embed-text-v1.5.f16.gguf
LLAMA_ARG_CTX_SIZE=2048
LLAMA_ARG_EMBEDDINGS=1
LLAMA_ARG_NO_WEBUI=1
docker compose up -d llama embeddingIf you build it with Docker before it will be faster, it will rebuild after you update llama.cpp submodule you can check the logs to see if everything's OK with
docker compose logs -fTabby
Back in docker-compose.yml, add this service :
tabby:
restart: always
env_file: .env.tabby
image: registry.tabbyml.com/tabbyml/tabby
command: serve
container_name: tabby
volumes:
- "$HOME/.tabby:/data"
- "$HOME/dev:/data/dev" # this is where you store your code
ports:
- 8082:8080
You need to add your token in the .env.tabby, you find it when you click on your profile picture on the top right of the tabby webapp, you must omit the "auth_" prefix
# .env.tabby
TABBY_WEBSERVER_JWT_TOKEN_SECRET=***Start the service with
docker compose up -d tabbyOpenWebUI
Finally, in docker-compose.yml, add this service :
webui:
env_file: .env.webui
restart: always
image: ghcr.io/open-webui/open-webui:main
container_name: webui
ports:
- 8083:8080
volumes:
- ./data/openwebui:/app/backend/data
In .env.webui :
OPENAI_API_BASE_URL=http://localhost:8080
You can now start the service with :
docker compose up -d webuiFull Tabby Compose stack
# docker-compose.yml
services:
llama:
build:
context: ./build/llama.cpp/
dockerfile: .devops/cuda.Dockerfile
env_file: .env.llama-qwen-14b
restart: always
container_name: llama
ports:
- 8080:8080
volumes:
- ~/llama-models:/models
deploy:
resources:
reservations:
devices:
- driver: nvidia
device_ids: ['0']
capabilities: [gpu]
embedding:
build:
context: ./build/llama.cpp/
dockerfile: .devops/cuda.Dockerfile
env_file: .env.embedding
container_name: embedding
restart: always
ports:
- 8081:8080
volumes:
- ~/llama-models:/models
deploy:
resources:
reservations:
devices:
- driver: nvidia
device_ids: ['0']
capabilities: [gpu]
tabby:
restart: always
env_file: .env.tabby
image: registry.tabbyml.com/tabbyml/tabby
command: serve
container_name: tabby
volumes:
- "$HOME/.tabby:/data"
- "$HOME/dev:/data/dev" # this is where you store your code
ports:
- 8082:8080
webui:
env_file: .env.webui
restart: always
image: ghcr.io/open-webui/open-webui:main
container_name: webui
ports:
- 8083:8080
volumes:
- ./data/openwebui:/app/backend/data
To keep this up to date, just :
docker compose pull tabby webui
git submodule update --recursive --init
# now restart the updated services, and rebuild llama.cpp if it was updated
docker compose up -d llama embedding tabby webuiWait, more ?
The former is a "software engineer" able to output full projects from user prompts, the latter is an image generation service that can run most open checkpoints like Stable Diffusion and Flux.1.
Bolt.diy
Okay, let's start : as for Llama.cpp, we will build Bolt and include it as a git submodule.
git submodule add https://github.com/stackblitz-labs/bolt.diy build/boltAdd a service in the compose file :
# docker-compose.yml > services
bolt:
image: bolt-ai:production
restart: always
container_name: bolt
build:
context: ./build/bolt/
dockerfile: Dockerfile
target: bolt-ai-production
ports:
- "8084:5173"
env_file: ".env.bolt"
environment:
- NODE_ENV=production
- COMPOSE_PROFILES=production
- PORT=5173
- VITE_LOG_LEVEL=${VITE_LOG_LEVEL:-debug}
- DEFAULT_NUM_CTX=${DEFAULT_NUM_CTX:-131072}
- RUNNING_IN_DOCKER=true
- OPENAI_LIKE_API_BASE_URL=http://llama:8080/v1
command: pnpm run dockerstart
profiles:
- production
Let's build and run it :
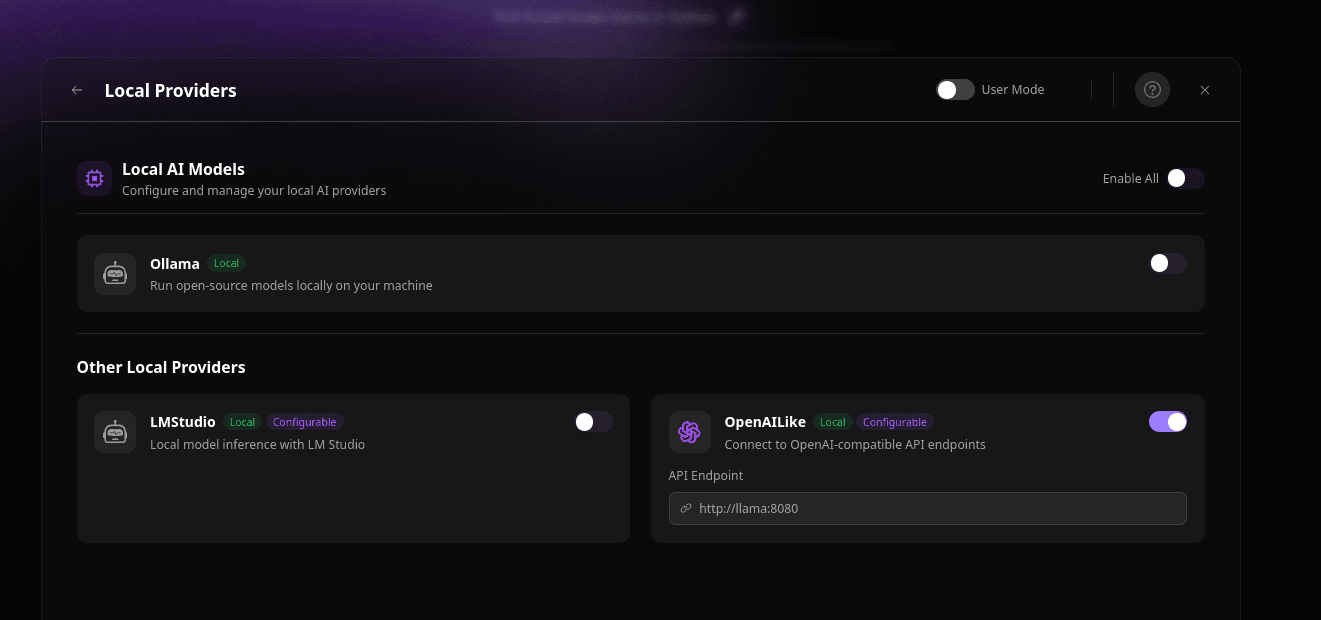
docker compose up -d bolt Once you head to http://localhost:8084 you need to enable the Local OpenAI like provide :
Find the cog in the bottom of the left sidebar, then Local Providers, and check OpenAILike, finally enter "http://llama:8080"
Finally select OpenAILike and input a prompt, and let the magic happen
ComfyUI
Comfy allow to create images, it has a nicer UI than stable-diffusion-webui and has a very cool plugin manager allowing to make complex things easy.
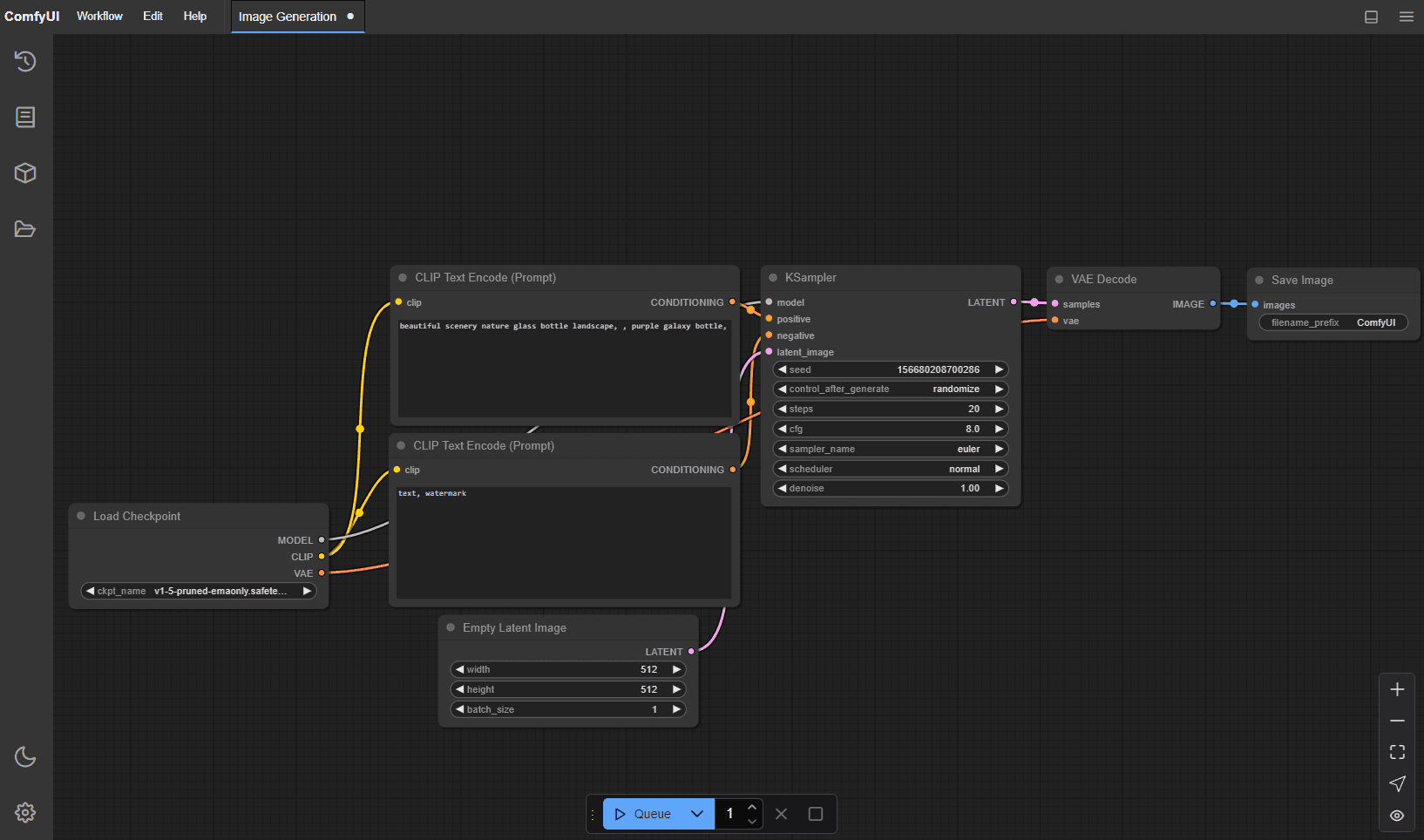
There is no official Docker image of Comfy but I found on the Github's discussions this project that publishes several images, some with included templates and models, that we are going to use.
There is a rocm build in case you use an AMD GPU, if you'll have to wait for a Vulkan implementation.
First, let's create the directory to host Comfy's data :
mkdir data/comfyNote the user key that matches my linux user UID (type id in a shell to know yours), that will prevent the volume to be mounted with root rights and will allow you to manually download checkpoints and loras in this directory.
I picked the "megapak" image that includes Flux.1 Schnell, I downloaded the Dev variant and put it in data/comfy/models/checkpoints to generate this post's illustration
# docker-compose.yml > services
comfy:
restart: always
image: yanwk/comfyui-boot:cu124-megapak
user: '1000'
volumes:
- ./data/comfy:/root
container_name: comfy
ports:
- 8084:8188
deploy:
resources:
reservations:
devices:
- driver: nvidia
count: 1
capabilities: [gpu]
Now, you know what to do :
# You may need to shut down llama to free VRAM
# docker compose down
docker compose up -d comfyIt will download a bunch of checkpoints before run, and even more after :) but you'll have a complete image gen tool.
To use Flux.1 in fp8 you need about 16-18 GB of VRAM, but there are many alternatives, like Stable Diffusion, etc.
You can head to their examples page, e.g: the Flux Schnell one, then drag and drop the image on your Comfy to import the full workflow.

The manager will prompt or you will be notified (I had both cases) you if you miss something and suggest you to download it. If it is some checkpoints just download them in data/comfy/models/checkpoints.
Of course you may have to choose between llama and comfy. I use Qwen Coder 32B that saturates my GPU, so I need to turn it off before I start comfy.
Have fun !
Sources
Maybe the best source when you are interested in local AI
Maybe the second best source
The amount of work there is over 9000
Great project, written in Rust so even greater
I think it's the best image generation tool
The open source fork, by the official team
